Bard is a generative AI-powered ChatBot released in March 2023 and developed by Google AI - Google's Artificial Intelligence research and development division. Powered by large language models(LLMs), it has been designed to understand and produce responses in a conversational human-like form.
Bard is a creative and helpful collaborator to supercharge your imagination, boost your productivity, and bring your ideas to life. - Google AI
The introduction of Bard made Google a major competitor in the new War of the Machines or LLM wars, similar to the highly debated AI voice assistant wars between Google's Assistant, Microsoft's Cortana, Apple's Siri, and Amazon's Alexa.
History&Development
It is popularly believed that Bard was quickly developed and released as an immediate response to the massive success and reception of Microsoft x OpenAI's AI chatbot, ChatGPT, released in November 2022. However, this is highly untrue, as the term "Bard" and its capabilities had already been mentioned in Google's public discourses as far back as 2019. Google Research also published a framework in 2020 on a conversational agent that could learn to produce responses on any topic.
Additionally, during Data Cloud & AI Summit, Google highlighted its immense contribution and championing of the development of LLMs from the very beginning; the creation of both the TPU and open-sourced Transformer technology, accelerated machine learning workloads and kickstarted the generative AI innovation. BERT, launched by Google, was the world's first breakout large language model, and unsurprisingly, GPT-3 which powered ChatGPT was built on Transformers.
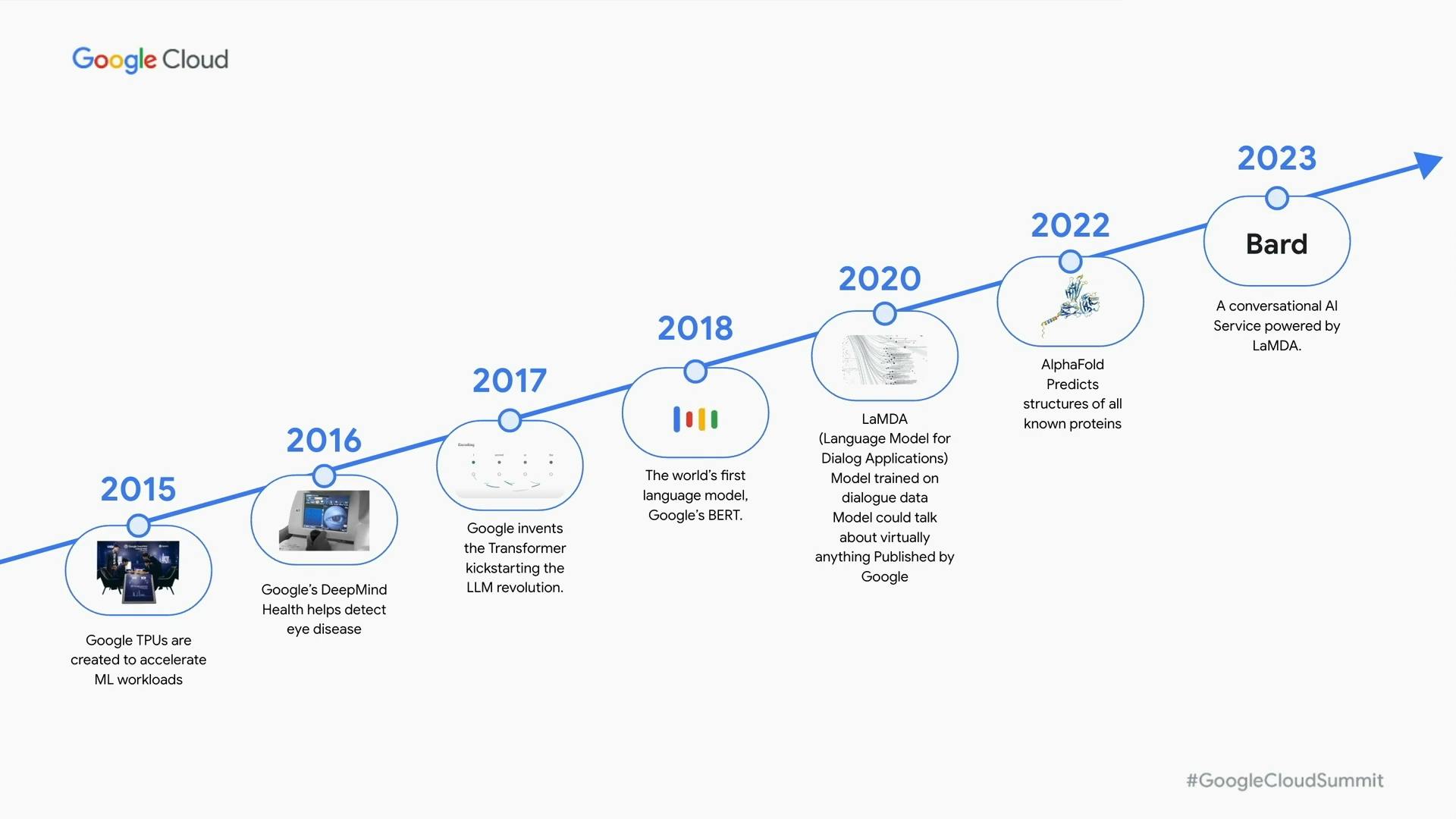
In 2017, Google shifted its entire company focus to being "AI First". This meant the integration of its entire portfolio, research and future developments with intelligent technology. Google AI was launched and eventually, AI-powered products and services were released including the Language Model for Dialogue Applications(LaMDA) LLM, a breakthrough conversational AI technology.

This led to the development of a conversational AI service called Bard, built on a lightweight and optimised version of LaMDA and trained on 1.56 trillion parameters from external and internal Google sources culminating in over 100 million webpages, books, articles and repositories (by its own assessment); additionally, with the ability to search the internet in real-time, it is able to give much more accurate and refined answers. The term "Bard", chosen to reflect the creative nature of its algorithm, originates from poets of historic Celtic origin, called Bards, who possessed unique imaginative and expressive abilities.
At the announcement at Google I/O 2023, an upgrade to the newest edition of the Pathways Language Model, PaLM 2 - Google's largest and most advanced language learning model, has significantly advanced the capabilities of Bard.
Working Process
By its own admission, Bard functions as a combination of natural language processing, knowledge representation and additional machine-learning techniques. This enables it to understand and give responses to prompts because it has broken down its trained text into component parts, such as words, phrases, and sentences, stored it in an accessible manner and identified patterns in the data. It can also give feedback on new information, identify factual errors, provide additional context, or suggest alternative interpretations.
In providing responses, Bard utilises context in prompts and other interactions within sessions to compose a variety of responses which are ranked according to safety parameters and re-ranked according to quality. With the highest-ranked response(s) displayed to the user in an informative, comprehensive, and personalized manner.
Using Bard

There are a wide variety of exciting possibilities with Bard, majorly in problem-solving, creativity, logical reasoning, and code generation. It can also be used to summarize web pages and articles, generate ideas and suggestions for content creation, make comparisons between items, compose messages, emails and proposals, give recommendations, quiz preparations and lots more.
Video Information
Accessibility
Bard is free and easy to use, for users above the age of 18, through bard.google.com. Accessing and utilising it requires a personal Google account and a supported browser. It is available in 180 countries and territories around the world and operates primarily in 3 languages English, Japanese and Korean. It accepts voice and text input prompts to conduct searches.
Bard vs Search
For the avoidance of doubt, Bard and Search are not the same. While they both have similarities in searching for and displaying information, Search is designed to find information on the web through keywords and Bard is designed to communicate and generate human-like text in response to a wide range of prompts and questions in a dialogue format.
Additional differences include the fact that Search is a factual search engine for showcasing authentic information and a single-purpose tool, while Bard's can be likened to a creative search engine, whose information may not necessarily be authentic but is able to generate information on the go as a multi-purpose tool.
An example with a prompt on "the recipe for making aloe vera juice", Bard produces an exact response whereas Search would give links to different websites.
“I just want to be very clear: Bard is not search.” "It is a collaborative AI service"
"The magic that we’re finding in using the product is really around being this creative companion to helping you be the sparkplug for imagination, explore your curiosity, etc."
“But as you want to get into more of the search-oriented journeys, we already have a product for that — it’s called search”
Jack Krawczyk, Product Lead, Google Bard
Google has explicitly stated that Bard and Search are not the same, and neither will Bard be replacing Search. Bard simply exists as a complementary service to Search to improve and enrich the information-gathering experience due to its intuitive and straight-to-the-point capabilities.
This is a sharp contrast to Microsoft x Open AI's approach, as they have launched an AI-powered copilot for the web, a conversational chat experience within the Bing search engine.
Challenges
Despite the global rollout and continuous upgrades, Bard is still labelled as an “experiment”. It is a direct interface to a large language model and not a source of factual information. Google also highlights that Bard’s responses cannot be relied on for medical, legal, financial or other professional advice.
The interface of Bard also contains more visible and clear caveats; an indemnity statement "Bard may display inaccurate or offensive information that doesn’t represent Google’s views" and a "Google It" button, alongside each response suggesting where accurate information can be found.
Privacy and Security
The development of Bard is strongly in line with Google's AI principles, launched in 2018, a guiding philosophy of its commitment to the responsible development of all technology in its portfolio. Bard is also designed to comply with privacy policies and data protection regulations, ensuring that user interactions and personal information are kept secure and confidential. A privacy notice describing how Google handles Bard data is publicly available and users are also allowed to manage their activity and adjust the settings to their satisfaction.

Although dedicated reviewers monitor Bard's conversations, Google also encourages users to indicate if Bard has been useful and helpful, by rating each response and providing additional feedback where necessary towards improving its capabilities.
Additionally, the American-based, Common Sense organisation, which helps parents and teachers make smart choices about learning tools for children, has rated Google Bard as 75% safe for usage(as of June 4, 2023). This rating is within the same range as other Google products: Classroom, Assistant, and Family Link; ChatGPT was rated as 45% safe for usage.
Into the Future
Bard is a top priority for Google. Ongoing efforts have been put in place and leading experts within Google have been directed to concentrate on developing Bard with newer features and curated experiences.
With the shift to PaLM 2, significant progress has been made in upgrading its mathematics, reasoning, creativity, and code generation capabilities to advanced levels, alongside deepening its general understanding of the world. Exciting new features have been announced and are expected shortly. These will be in visual responsiveness, prompting with images through Google Lens, coding upgrades, text-to-image generation and integrations with tools and extensions to access services from Google's apps and external software providers.
Detailed updates and blog posts on new possibilities with Bard are regularly released by Google.
Bard is the next generation of Artificial Intelligence.
Try Bard. bard.google.com.